Digging through your garden, you come across tunneled dirt and upturned mounds of earth. Who could be responsible for this mess? You might have suspected gophers, but the likelier culprit is the elusive mole. These subterranean pests not only wreak havoc on your lawn, but also on your precious root systems. Understanding the causes and effects of mole damage on root systems is crucial for any gardener hoping to maintain a healthy garden. In this article, we will explore the intricate web of factors that lead to mole damage, as well as the telltale signs of their presence, and the best prevention and control methods available. So, read on to take your first step towards a mole-free, thriving garden.
The Causes of Mole Damage on Root Systems
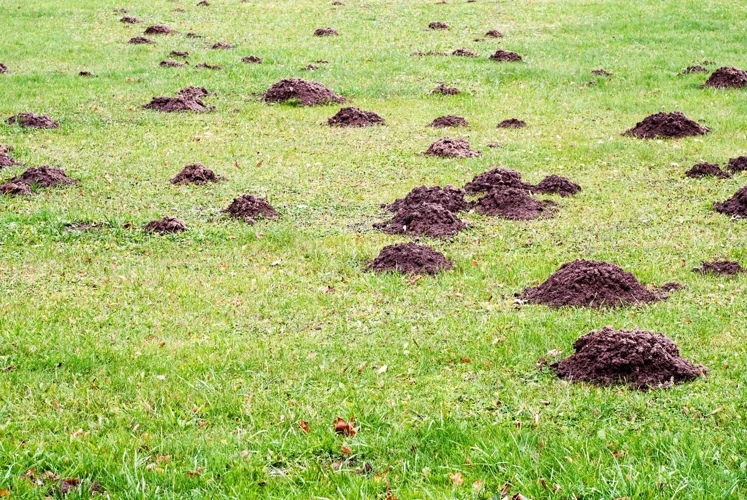

The presence of moles in your lawn, garden, or flower beds may seem harmless at first, but these small creatures can actually cause significant damage to root systems. Understanding the causes of mole damage can help you take proactive steps to prevent it. Moles can damage root systems in a variety of ways, including their activities, diet, and habitat. By identifying these causes, you can better protect your plants from harmful mole damage. Later in this article, we will delve deeper into these causes, providing helpful tips on how to prevent and control mole damage on root systems. To learn more about identifying mole burrows in your yard, check out our article on mole burrow identification or how to distinguish mole damage from other pests on your lawn, see our article on mole damage vs other pests on the lawn.
1. Mole Activities
Moles are insectivorous mammals that live underground and can be found in many parts of the world. Their activities can have a significant impact on root systems, causing damage that may affect the health and growth of plants.
Tunneling: Moles burrow through soil in search of insects, grubs, and other small creatures that make up their diet. While tunneling, they may disturb root systems, causing roots to become dislodged or damaged. This can lead to reduced nutrient uptake and growth capabilities for plants in the area.
Soil upheaval: As moles dig and burrow, they can cause soil upheaval, leading to a lumpy, uneven surface that can make mowing and other maintenance tasks difficult. This can also cause soil erosion and compaction, further damaging root systems and affecting plant health.
Disturbed soil: Moles may also disturb the soil’s natural structure, breaking up clumps and loosening soil in patches. This can reduce the soil’s ability to hold water, essential nutrients, and oxygen, resulting in reduced root growth and increased susceptibility to damage.
To prevent mole activities from damaging root systems, it’s essential to take steps to control their presence in the area. Prevention tips can be found on our page about mole damage prevention. Additionally, if mole damage has already occurred, it may be necessary to repair the lawn or garden affected by using techniques explained on repairing lawn damage caused by moles, or by using traps and baits explained on benefits and drawbacks of different types of traps for mole removal. Repellents for aging mole control can be found on our page about mole control repellents. It is essential to consider mole damage to underground utilities explained on our page about mole damage to underground utilities.
2. Mole Diet
Moles are small burrowing animals with pointed snouts and large, powerful front claws. Their diet consists mainly of earthworms, grubs, and other soil-dwelling insects. However, moles may also feed on vegetation roots, bulbs, and tubers in search of insects.
To understand the mole’s diet more clearly, let’s take a look at the following table:
| Common Foods | Description |
|---|---|
| Earthworms | Moles prefer earthworms, and can consume their body weight in earthworms on a daily basis. They eat almost any species of earthworm and prefer larger, deeper-living earthworms that are found in the lower soil layers. |
| Grubs | These are the larvae of beetles and are found in the upper soil layers. Moles can also eat other larvae, such as cutworms, wireworms, and leatherjackets. They can easily detect them by their strong sense of smell. |
| Vegetation Roots | Moles may disturb the roots of plants while digging, leading to wilting or yellowing of the plants. Although this is rare, it can happen in gardens or flower beds with rich soil and high organic matter. |
| Nuts and Seeds | Moles may occasionally eat nuts and seeds, but this is not common in their diet. |
| Small Invertebrates | Moles consume many different types of invertebrates, such as ants, spiders, snails, and slugs. However, these make up a small percentage of their diet. |
It’s essential to note that although moles primarily feed on insects, their burrowing activities and rooting for food can cause significant damage to plants and soil structure. This will be discussed further in the following section on the Effects of Mole Damage on Root Systems.
If left uncontrolled, mole damage can severely impact the health of grass and other plants in the garden and lead to a decline in lawn health. In the next section, we will discuss the effects of mole damage on root systems.
3. Mole Habitat
Moles are small mammals that are part of the Talpidae family. They are found in different regions of the world and are known for their subterranean lifestyle. Understanding the habitat of moles is important in identifying the risk of potential mole damage on root systems.
|Mole Habitat Characteristics |Description |
|—|—|
|Soil| Moles prefer to live in soil that is moist, well-drained, and rich in organic matter. They create burrows in soil that has a high percentage of humus, which is a layer of decomposed plant material.|
|Shelter| Moles avoid direct sunlight and prefer to burrow in areas with shade or near the roots of plants where there is cover.|
|Food| Moles eat insects such as earthworms, grubs, and beetle larvae as well as other small animals like mice and shrews.|
|Location| Moles can be found in many different habitats including grass fields, gardens, orchards, and forests. |
Moles prefer to burrow in soil that is rich in organic matter because of the abundance of food sources such as earthworms, grubs, and beetle larvae. These insects are beneficial to the soil but their presence can also attract moles to the area. The Lawn & Garden can be at risk of mole damage because of the abundance of earthworms in the soil.
Moles require shelter from direct sunlight and prefer to burrow in areas with shade or near plant roots. The roots provide cover and protection from predators. In gardens and flower beds, moles can burrow near plant roots and cause damage to the root system. This can lead to stunted plant growth and reduced nutrient absorption in the plants.
Understanding the habitat of moles is important in identifying the areas at risk of mole damage on root systems. Knowing this information can help in the prevention and control of mole damage.
The Effects of Mole Damage on Root Systems

The activity of moles in gardens and flower beds can lead to extensive damage on root systems of plants. This can have negative effects on the growth and health of the plants, ultimately leading to reduced yields and stunted growth. Understanding the effects of mole damage on root systems is crucial in devising effective prevention and control measures to ensure optimal plant growth. The following sections will explore the various effects of mole damage on root systems in detail.
1. Soil Erosion and Compaction
Soil erosion and compaction are among the most evident effects of mole damage on root systems. When moles burrow underground, they create tunnels that loosen the soil and leave empty spaces in their wake. As rainwater seeps into the soil, it washes away soil particles and sediments along the tunnels, resulting in erosion. Eroded soil can become unstable, making it harder for plants to grow and causing them to lose their anchoring and support system.
As moles tunnel through the soil, they can cause compaction, which refers to the crushing of soil particles. Soil compaction makes it difficult for roots to absorb water and nutrients necessary for plants’ growth. It also hinders the passage of water, air, and organic matter necessary for maintaining a healthy soil ecosystem.
If left unchecked, soil erosion and compaction can lead to several problems in gardens and flower beds, such as waterlogging, nutrient depletion, plant suffocation, and root rot. To prevent these issues, it is essential to address mole damage promptly and implement appropriate measures to prevent further damage to the root systems.
Experts recommend regularly checking that the soil drainage system in the garden is functioning correctly, and the soil is well aerated. Gardeners can add organic matter, such as compost or mulch, to the soil to boost its structure and encourage the growth of beneficial microorganisms. By doing so, they can reduce soil erosion and compaction caused by mole activity and improve the soil ecosystem’s overall health.
2. Reduced Nutrient Absorption
Mole damage to root systems can lead to reduced nutrient absorption, which is essential for the growth and development of plants. This can occur due to a number of factors, including the physical disruption of roots caused by mole tunnels and the loss of fine roots that are responsible for nutrient uptake.
Here are some of the ways that reduced nutrient absorption can impact plants:
- Stunted growth: Without sufficient nutrients, plants may struggle to grow to their full potential. This can result in stunted growth, where the plant is smaller than it should be for its age.
- Poor fruit or flower production: Plants need nutrients to produce flowers and fruit. If they are not getting the nutrients they need, their production may be limited, resulting in fewer or smaller flowers or fruit.
- Yellowing leaves: Nutrient deficiencies can cause leaves to turn yellow or brown. This is because plants need certain nutrients to produce chlorophyll, which is responsible for their green color. When plants don’t have enough of these nutrients, their leaves can’t produce enough chlorophyll and will start to yellow or brown.
- Vulnerable to disease: Plants that are not getting the nutrients they need are more vulnerable to disease and pests. This is because they are not as healthy and their immune systems are weakened.
To mitigate the effects of reduced nutrient absorption from mole damage, it is important to address the root cause of the problem, which is the mole activity. Preventing moles from damaging roots in the first place through physical barriers, repellents, traps or professional mole control is essential to ensure that plants have the chance to grow and thrive.
3. Stunted Growth and Limited Root Expansion
Stunted growth and limited root expansion are some of the most devastating effects of mole damage on root systems. Moles tend to tunnel through the soil, disrupting and damaging roots in the process. As a result, plants struggle to absorb nutrients and water from the soil, leading to limited growth potential and stunted development.
The following table highlights some of the specific ways in which mole damage can impact plant growth:
| Effect of Mole Damage on Root System | Impact on Plant Growth |
|---|---|
| Root Pruning | Restricted nutrient and water uptake, limited root expansion, poor growth |
| Soil Compaction | Reduced aeration and drainage, restricted root growth and nutrient uptake, stunted growth |
| Reduced Soil Depth | Restricted root growth, reduced nutrient and water uptake, stunted growth |
Mole damage can have a significant impact on the ability of plants to thrive, reducing their growth potential and limiting their productivity. As such, it is important to take steps to prevent and control mole activity in areas where plants are present.
Signs of Mole Damage on Root Systems

When it comes to identifying mole damage on root systems, there are certain signs that you should be on the lookout for. These subtle indicators can often be easy to miss or confuse for something else, which can lead to further damage to your plants and soil. It’s important to know what to look for so that you can take action as soon as possible. Let’s take a closer look at some of the telltale signs that moles have been causing damage to your root systems.
1. Tunnels in the Soil
One of the telltale signs of mole damage on root systems is the presence of tunnels in the soil. These tunnels are created by moles as they burrow through the soil in search of food and shelter. The tunnels have a distinct ‘mole’ shape, with raised ridges that run along the top of the tunnel. This is because moles push the soil up as they dig their tunnels.
These tunnels can cause several problems for plants and their root systems. First, as moles dig tunnels, they move soil from one location to another, which can disrupt the soil’s natural structure and composition. This, in turn, can lead to soil erosion and compaction, which can make it more difficult for roots to grow and absorb nutrients.
The raised ridges from mole tunnels create air pockets in the soil, which can dry out plant roots and damage them. This can lead to wilting and yellowing of leaves, as well as stunted growth. The tunnels themselves can also prevent water and nutrients from being distributed evenly throughout the soil, leaving some areas of the root system without the resources they need to grow.
Overall, tunnels in the soil are a clear sign of mole damage to root systems and should be addressed promptly. If you notice tunnels in your soil, it’s important to take action to prevent further damage to your plants and their root systems.
2. Molehills
One of the most visible signs of mole activity is molehills. These are small mounds of soil that are raised above the surface of the ground. Molehills are created as moles dig their tunnels and push the excess dirt up to the surface.
Molehills can cause a number of problems for root systems, including changes in soil structure and drainage issues. When molehills are present, they can act as a barrier to water and nutrients, preventing them from reaching the roots. This can cause reduced nutrient absorption and stunted growth of plants.
Molehills can also lead to soil erosion and compaction. As the soil is pushed up to the surface, it can become loose and dry, making it more susceptible to wind and water erosion. Additionally, the soil movement caused by moles can lead to areas of the soil becoming compacted, making it difficult for plants to grow and for water to penetrate the ground.
If you notice molehills in your lawn or garden, it is important to take action to prevent further damage to the root system. This can include physical barriers such as installing mesh or fencing, as well as using mole repellents or traps. In some cases, it may be necessary to seek the assistance of professional mole control services.
While molehills may seem like a minor annoyance, they can have significant effects on the health and growth of root systems. By being vigilant and taking proactive steps to prevent and control mole damage, you can ensure that your plants and trees remain healthy and thrive.
| Signs of Mole Damage on Root Systems | Causes | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Tunnels in the Soil | Mole Activities, Mole Diet, Mole Habitat | Soil Erosion and Compaction, Reduced Nutrient Absorption, Stunted Growth and Limited Root Expansion |
| Molehills | Mole Activities, Mole Diet, Mole Habitat | Soil Erosion and Compaction, Reduced Nutrient Absorption, Stunted Growth and Limited Root Expansion |
| Wilting or Yellowing Plants | Mole Activities, Mole Diet, Mole Habitat | Soil Erosion and Compaction, Reduced Nutrient Absorption, Stunted Growth and Limited Root Expansion |
3. Wilting or Yellowing Plants
Plants rely on their root systems to absorb nutrients and water from the soil. When moles damage these root systems, the plants may struggle to survive. One of the signs of mole damage on root systems is wilting or yellowing plants.
This happens because the damaged roots are unable to absorb enough water and nutrients to support the plant’s growth. As a result, the leaves may droop or wilt, and the plant may turn yellow as it struggles to produce chlorophyll. In severe cases, the plant may die.
It’s important to note that not all wilting or yellowing plants are a sign of mole damage. Other factors, such as overwatering or disease, can also cause these symptoms. However, if you notice wilting or yellowing plants in conjunction with other signs of mole damage, it may be worth investigating further.
If you suspect that moles are causing damage to your root systems, it’s important to take action to prevent further harm. Consider using physical barriers, repellents, traps, or professional control methods, as discussed in earlier sections of this article. By taking swift and effective action, you can help protect your plants from the damaging effects of mole activity.
Prevention and Control of Mole Damage on Root Systems
As gardeners, we want to ensure that our plants grow healthy and strong, but mole damage on root systems can be a significant hindrance. Taking preventative measures and controlling the presence of moles can help maintain healthy roots and soil. From physical barriers to professional mole control, there are several prevention and control methods to consider. In this section, we will go over the various ways of addressing mole damage on root systems and maintaining a thriving garden.
1. Physical Barriers
Physical barriers can be an effective way to prevent moles from damaging root systems. These barriers work by creating a physical obstacle that the moles cannot easily pass through.
One option for a physical barrier is to install a wire mesh around the area where the root system is located. The mesh should be buried a few inches underground and extend several inches above the surface to prevent moles from burrowing underneath it or jumping over it. Another option is to use a root barrier, which is designed to prevent roots from growing into unwanted areas. It can also serve as a physical barrier to keep moles from accessing the root system.
Stone barriers, such as large rocks or bricks, can also be effective. These can be placed in a line around the root system, creating a barrier that is difficult for moles to navigate. Additionally, garments can be used as a physical barrier, such as placing plant pots with smooth sides or wrapping tree trunks with a metal band.
| Physical barriers | How they work | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wire mesh | Creates an underground and above ground physical barrier to prevent moles from passing through. | Long-lasting and effective. | May be difficult to install in existing landscapes. |
| Root barrier | Designed to prevent roots from growing into unwanted areas and keep moles from accessing the root system. | Multi-functional, as it also helps control root growth. | Can be costly to install. |
| Stone barriers | Large rocks or bricks create a barrier that is difficult for moles to navigate. | Natural-looking and long-lasting. | May be heavy and difficult to install. |
| Garments | Smooth surfaces create a barrier that is difficult for moles to climb or navigate. | Can be a cost-effective solution. | May not be as effective as other physical barriers. |
It is important to note that a physical barrier may not be a foolproof solution, as moles can be persistent and find ways to dig underneath or around the barrier. It is recommended to use a combination of prevention and control methods to effectively manage mole damage on root systems.
2. Repellents
One option for preventing mole damage on root systems is through the use of repellents. Repellents work by producing an odor or taste that repels moles, making them less likely to tunnel and forage in the area. However, it is important to note that repellents may not be effective in all situations and may need to be reapplied regularly.
There are several types of mole repellents available, including:
- Castor oil-based repellents: These repellents work by emitting an odor that moles dislike. They are typically applied to the soil and can last for several weeks. However, they may also repel beneficial insects and earthworms.
- Plant-based repellents: These repellents utilize plant oils, such as peppermint or garlic, to produce an odor that repels moles. They are typically available as spray or granular applications and may need to be reapplied often.
- Sonic repellents: These repellents emit a high-frequency sound that is unpleasant to moles. However, their effectiveness is questionable and they may also disturb pets and wildlife.
- Mothball repellents: These repellents are not recommended, as they contain toxic chemicals that can harm pets and wildlife.
It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying repellents and to choose a product that is safe and effective for your specific situation. Additionally, repellents may work best when used in combination with other mole control methods, such as physical barriers or traps. Always monitor your garden regularly to ensure that mole damage is not occurring despite the use of repellents.
3. Traps and Baits
One effective method for controlling mole damage on root systems is through the use of traps and baits. There are several types of traps and baits available that can be used to catch moles in the yard or garden.
1. Live Traps: Live traps are a humane method of trapping moles. These traps are designed to capture the mole unharmed and can then be released in a different area away from the garden. Live traps should be checked frequently and the captured moles should be released as soon as possible.
2. Lethal Traps: Lethal traps are designed to kill moles instantly. These traps can be effective but should be used with caution to avoid harming other wildlife. It is important to follow the instructions carefully and to check the traps regularly.
3. Baits: Poison baits can be effective for controlling moles, but they should be used with caution as they can also harm other wildlife or pets. It is important to place the bait carefully and to follow the instructions on the package.
When using traps and baits to control mole damage, it is important to monitor the success of the method and to make adjustments as necessary. It may be necessary to try a different type of trap or bait if the first attempt is not successful. It is also important to follow safety guidelines and to avoid harming other wildlife or pets in the process.
4. Professional Mole Control
Professional mole control can be a highly effective method for getting rid of moles and preventing further damage to root systems. This approach typically involves hiring pest control experts who have the necessary training and equipment to deal with mole infestations. Here are some of the main advantages of professional mole control:
| Advantages | Description |
| Expertise | Pest control professionals have extensive knowledge and experience in dealing with mole infestations. They can accurately identify the extent of the problem and determine the best course of action. |
| Efficiency | Professional mole control is often much more efficient than DIY methods since pest control experts have access to specialized equipment and techniques. |
| Safety | Hiring professionals ensures that the removal process is safe for both humans and pets. Pest control experts use humane and environmentally-friendly methods that do not harm the surrounding ecosystem. |
| Guarantee | Many pest control companies offer guarantees for their services, which means that they will continue to work on the problem until it is completely resolved. |
Professional mole control can be an effective solution for addressing mole damage on root systems. However, it is important to select a reputable pest control company and understand the costs and limitations of this approach before moving forward.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mole damage on root systems can have negative effects on plants and the overall health of a garden or yard. It is caused by a combination of factors, including mole activities, diet, and habitat. The effects of mole damage on root systems include soil erosion and compaction, reduced nutrient absorption, and stunted growth and limited root expansion.
Fortunately, there are signs that can be observed to determine if a garden or yard is experiencing mole damage, such as tunnels in the soil, molehills, and wilting or yellowing plants. Preventative measures can also be taken to minimize mole damage, such as physical barriers, repellents, traps and baits, or professional mole control.
It is important to take action when signs of mole damage are detected, as the health of plants and the overall appearance of a garden or yard can be significantly impacted. With proper preventative measures and timely intervention, the negative effects of mole damage on root systems can be mitigated, allowing for a healthy and thriving outdoor space.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can moles damage root systems in gardens or farms?
Yes, moles can cause significant damage to root systems in gardens and farms by disrupting the soil and feeding on roots.
2. Why do moles create tunnels in the soil?
Moless create tunnels in the soil to forage for food, such as earthworms and grubs, and to create their underground homes.
3. Can mole damage lead to plant wilting or yellowing?
Yes, mole damage can cause plant wilting or yellowing due to disrupted root systems and reduced nutrient uptake.
4. Are there any physical barriers that can prevent mole damage?
Yes, physical barriers such as mesh wire or underground fencing can prevent moles from accessing a certain area.
5. Can repellents effectively deter moles from an area?
Some repellents may deter certain moles, but they are not always effective and may need to be reapplied frequently.
6. Are traps and baits humane ways to deal with moles?
Traps and baits designed for moles can be humane, but it is important to follow instructions carefully and ensure that the mole is killed quickly and without undue suffering.
7. Can soil erosion and compaction caused by moles be fixed?
Yes, soil erosion and compaction can often be remedied by aerating the soil and adding organic matter.
8. Is professional mole control necessary for severe infestations?
Severe infestations may require professional mole control to effectively eliminate the problem.
9. Do moles respond to certain types of bait?
Some moles may be more attracted to specific types of bait, such as earthworms or beetle larvae, but this can vary by species.
10. How can mole damage affect the overall health of a plant?
Mole damage can restrict nutrient uptake and root growth, leading to stunted growth, wilting, and overall decreased plant health.