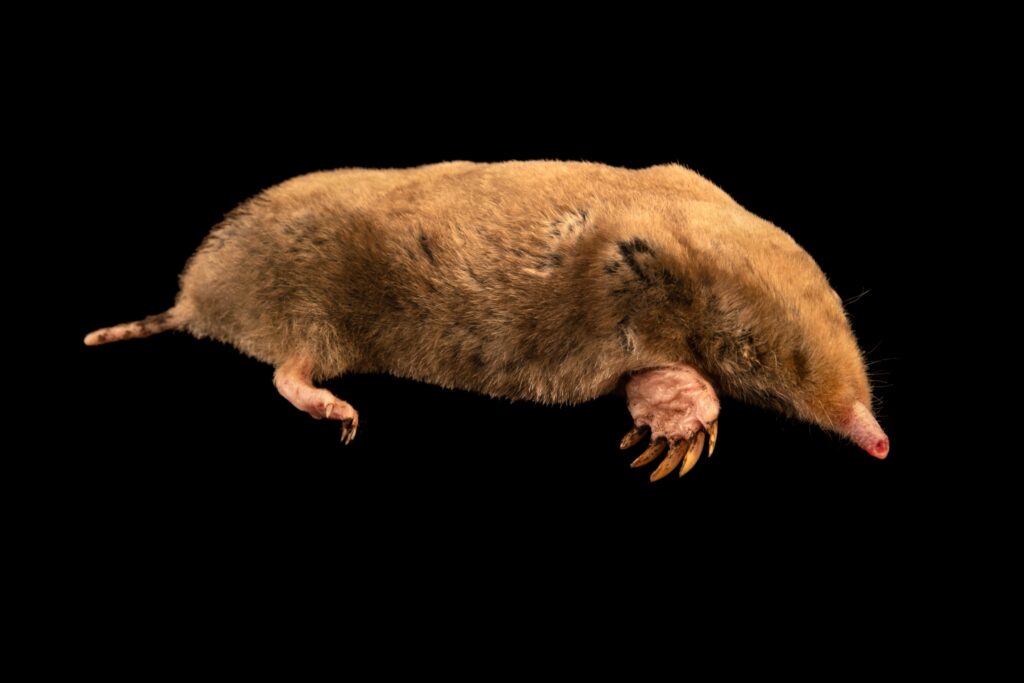
Do you ever wonder if moles have eyes? If so, you’re not alone. Many people are curious to know whether or not moles have eyes. The answer is both yes and no. Moles do have eyes, but they are very small and not visible to the naked eye. In this article, we’ll explore more about the eyes of moles and what you need to know.
Anatomy of the Mole
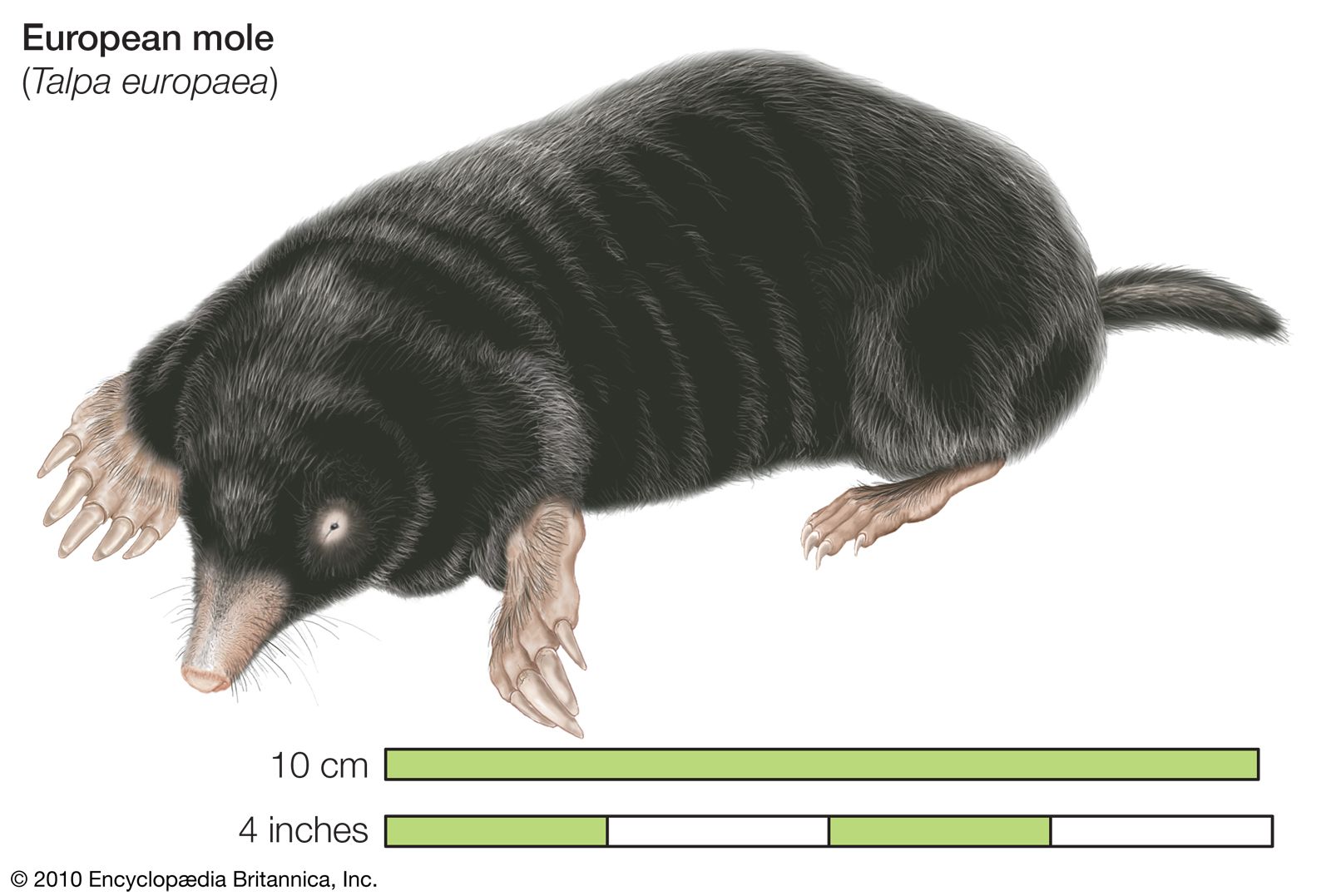
- Head: The head of a mole is small and pointed and is equipped with two very small eyes, covered by fur, which render them blind. The eyes are used to detect changes in light.
- Body: The body of a mole is cylindrical and is covered with short, velvety fur. The body length of an adult mole is approximately 3-6 inches.
- Limbs: A mole has four limbs, two of which are short, stout forelimbs, which are used for digging. The hind limbs are longer and are used for locomotion.
- Tail: The tail of a mole is short, measuring approximately 1 inch in length.
- Nose: The nose of the mole is very sensitive and is used to detect vibrations in the earth.
- Ears: The ears of a mole are small and are located just behind the eyes. The ears are used to detect low-frequency sounds.
Moles have poor eyesight due to the small size of their eyes and the fact that they are covered in fur, making them blind. Despite this, they possess a highly developed sense of touch and hearing. They are also equipped with two forelimbs that are adapted for digging and burrowing.
Do Moles Have Eyes?

Moles are small, burrowing mammals that are known for their underground tunnels and distinctive fur. While they are not blind, they do have some interesting physical characteristics that set them apart from other animals.
Do moles have eyes? Yes, moles have eyes, but they are very small and don’t provide much vision. Their eyes are covered by fur and skin, and they rely more on their other senses, such as smell and hearing, to find their way around.
- Moles have two small eyes under a layer of fur and skin.
- The eyes are about the size of a pinhead and can only detect light and movement.
- Moles rely more heavily on their sense of smell and hearing than their vision.
- Moles have adapted to living in the dark, so their vision isn’t as important for their daily lives.
- Despite having eyes, moles are not blind and can still detect light and motion.
Is a mole blind? No, moles are not blind. They are able to detect light and movement, but they rely more heavily on their sense of smell and hearing. Their eyes are small and don’t provide much vision, but they still play a role in the mole’s life.
Do Moles Have Other Senses?
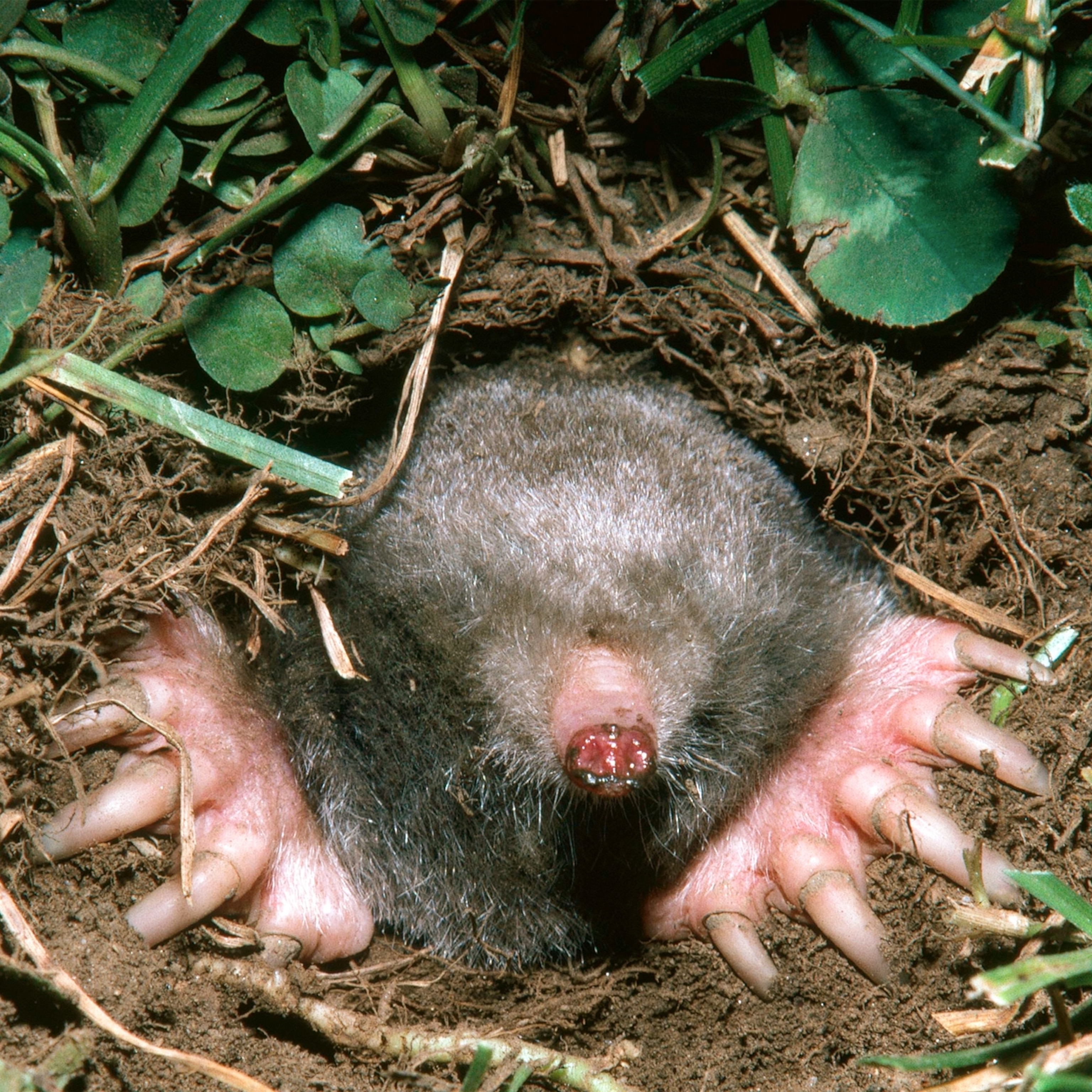

| Sensory System | Mole Senses |
|---|---|
| Hearing | Moles are not known to have any hearing. |
| Smell | Moles have a highly developed sense of smell. |
| Touch | Moles have sensitive whiskers and hairs on their body that help them detect movement and vibrations. |
| Taste | Moles have a sense of taste and use it to distinguish between different types of food. |
Moles rely on other senses besides sight to survive. They use their sense of smell to find food, detect danger, and identify other moles. They have sensitive whiskers and hairs on their body which they use to detect movement and vibrations. Moles also have a sense of taste which they use to distinguish between different types of food. However, they are not known to have any hearing.
How Does a Mole Navigate Its Environment?
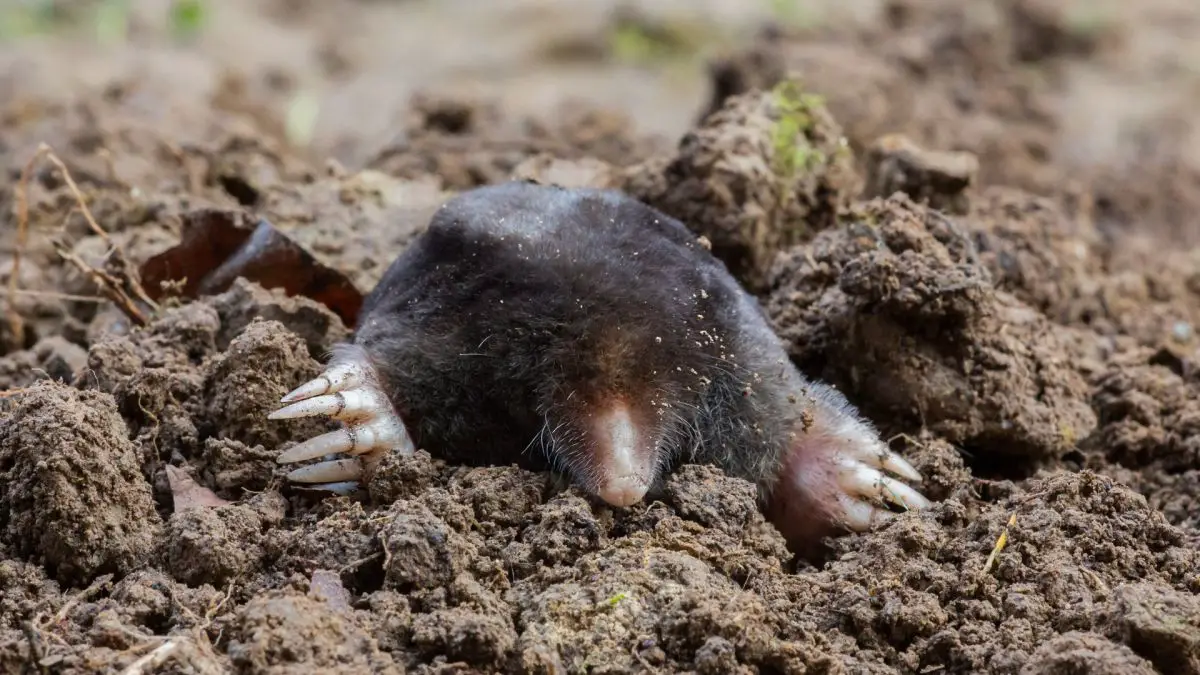

Moles lack eyes, so they have to rely on other senses to navigate their environment. They make use of:
- Smell: Moles have a well-developed sense of smell, and use it to locate food and other moles.
- Touch: Moles have sensitive whiskers on their faces which they use to feel their environment.
- Sound: Moles have sensitive ears, which they use to detect movement and other sounds.
Moles are also known to be able to sense vibrations in the ground, which they use to locate food and other moles. This is also how they are able to find their way through their tunnels.
Finally, moles use their sense of smell to detect the presence of predators, and the direction of their movements. This helps them avoid predation.
How Does a Mole Hunt for Food?
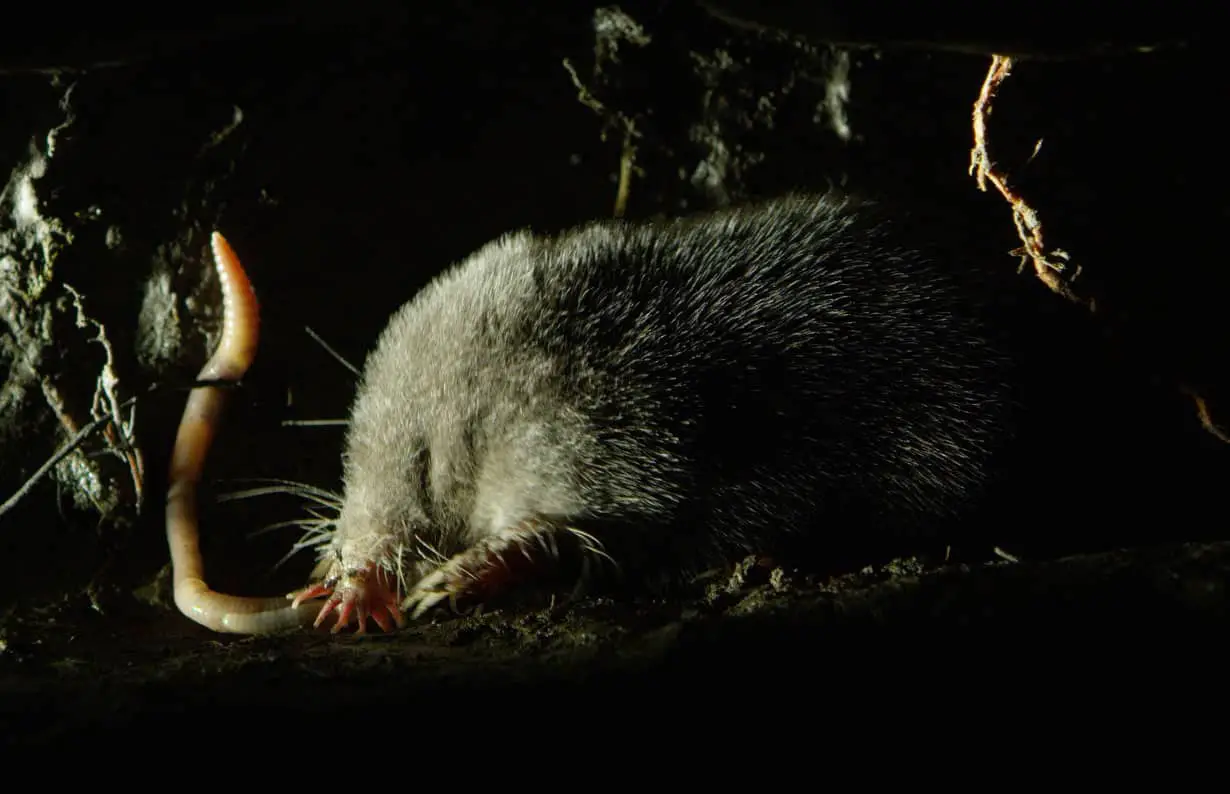

Moles are small mammals that primarily use their sensitive snouts, which are covered in whiskers, to search for food. They can detect vibrations in the soil and use the sensitive hairs on their snouts to identify food sources. They use their strong claws to dig small tunnels near the food source and then capture the food using their powerful jaws.
Moles mostly eat insects, worms, and other invertebrates, but they will also consume plant material such as roots and tubers. They can also feed on small mice, frogs, and reptiles if they come across them.
Moles are active both during the day and night and do not hibernate. When they are not hunting for food, they can be found in their underground tunnels. They use these tunnels to hide from predators and to store food for later consumption.
Moles are well adapted to their underground lifestyle and are able to survive in a wide range of habitats, from grasslands to forests. They are also quite resourceful and will make use of whatever food sources they can find.
How Does a Mole Avoid Predators?
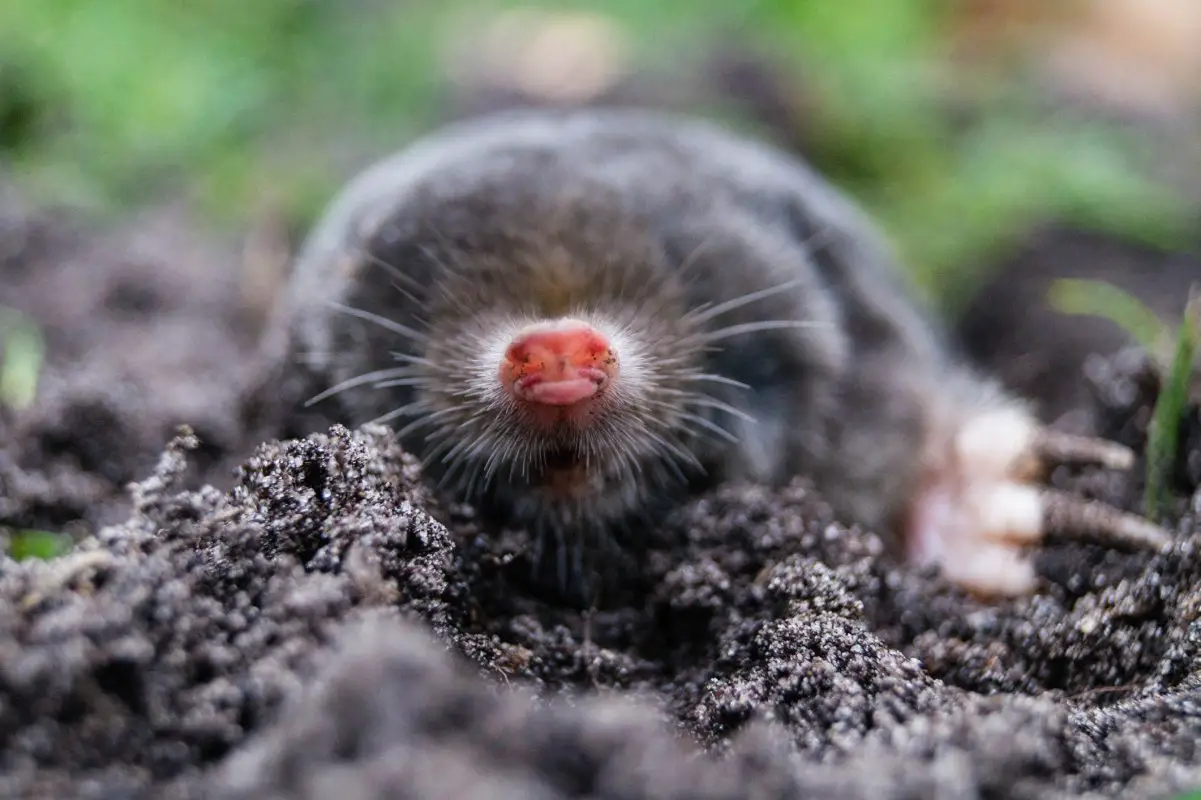

- Burrowing: Moles use their powerful front claws to dig tunnels and burrows in the ground to make a safe home.
- Camouflage: Moles have a dark brown or black fur that helps them blend in with their underground environment.
- Nocturnal: Moles are mostly active at night, which helps them avoid predators.
- Alertness: Moles have a keen sense of hearing and smell, allowing them to detect potential danger.
- Speed: Moles are fast and agile, allowing them to quickly escape predators.
Do Moles Have Other Adaptations?
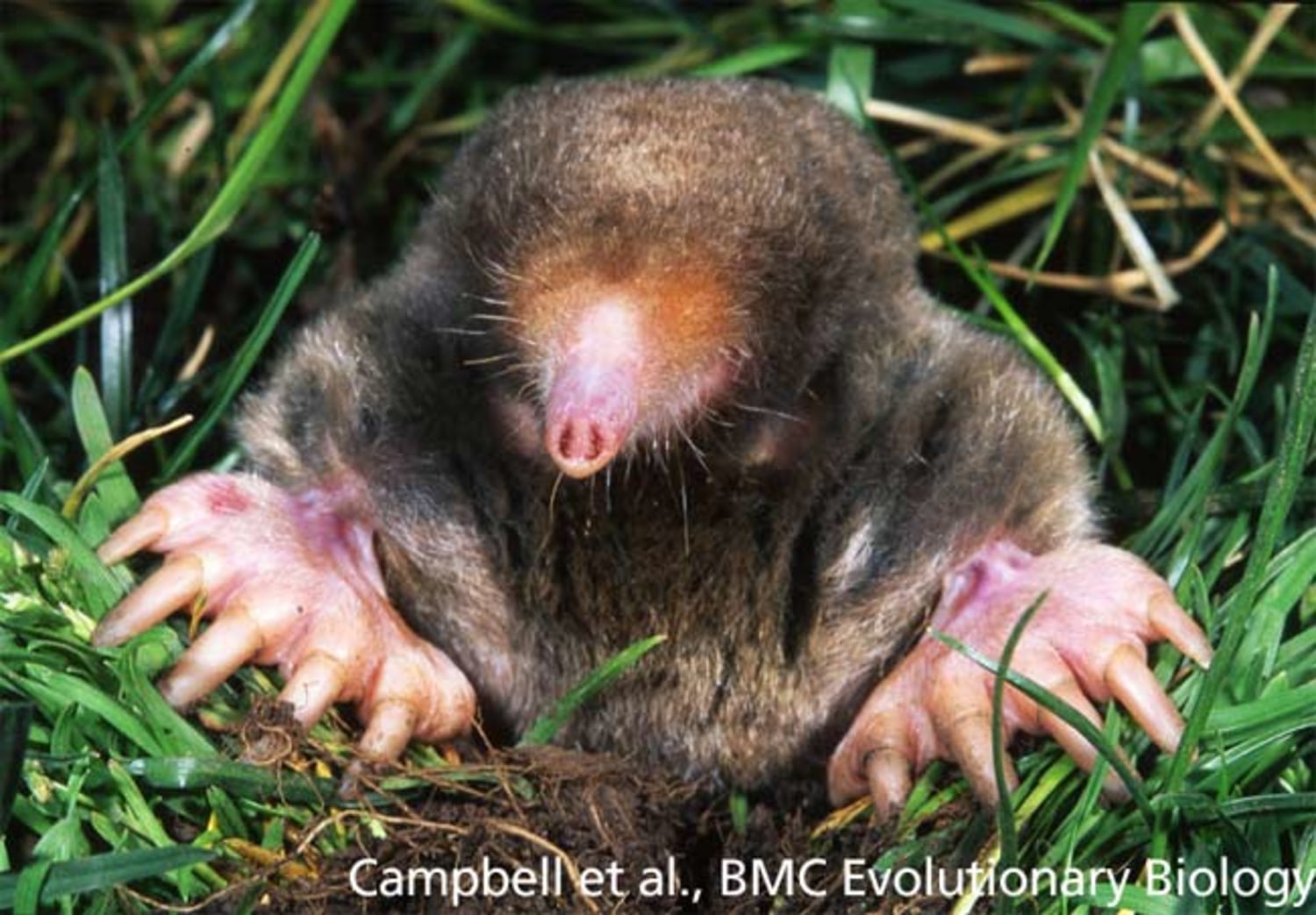

Moles are small, burrowing mammals that have several adaptations that make them well-suited to life underground. Although moles do not have eyes, they have several other adaptations that allow them to navigate and survive in their subterranean environment:
- Sensitive Whiskers: Moles have long, sensitive whiskers that help them to locate food and navigate around their dark environment. The whiskers also help them to identify predators and avoid them.
- Strong Claws: Moles have strong claws that they use to dig and burrow through the soil. The claws also act as a form of defense against predators.
- Excellent Hearing: Moles have excellent hearing, which helps them to detect predators and prey. The hearing also helps them to orient themselves in their dark environment.
- Enhanced Sense of Touch: Moles have an enhanced sense of touch, which helps them to detect vibrations in the soil. The sense of touch also helps them to identify food sources.
- Webbed Feet: Moles have webbed feet that help them to move quickly through the soil. The webbing also helps them to remain stable when digging and burrowing.
While moles do not have eyes, their other adaptations make them well-suited to life underground. These adaptations allow them to find food, navigate around their environment, and avoid predators.
Are There Different Types of Moles?
Yes, there are different types of moles. While all moles generally look quite similar, they can vary in shape and size. Moles can be round, oval, flat, or raised. They can also vary in color from light brown to black.
Most moles are non-cancerous, but some may be precancerous. The National Cancer Institute recommends that you have your moles checked by a doctor if they have any of the following characteristics:
- Larger than a pencil eraser
- Irregular edges
- Different colors
- Itchiness
- Bleeding or oozing
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Congenital (birth) moles | These moles present at birth or appear shortly after. |
| Acquired moles | These moles appear after birth and may increase in number with age. |
| Atypical moles | These moles are larger than average and may have an irregular shape or color. They are also known as dysplastic nevi and may be a sign of increased risk of skin cancer. |
It is important to note that moles have no eyes and are therefore blind, so they cannot see what is happening around them. However, moles can sense light and vibrations, which helps them locate food and avoid predators.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of moles?
- Moles are burrowing animals, so they dig tunnels and chambers to create a system of underground passages.
- Moles are important for aerating the soil and helping to keep the earth’s surface from becoming compacted.
- Moles are active predators and feed on many kinds of small invertebrates, such as earthworms and grubs.
- Moles also help to control the population of these small animals, which can be important for maintaining a healthy ecosystem.
- Moles can also play an important role in seed dispersal by carrying and burying seeds in their burrows, which can help to spread plants to new areas.
Are Moles Blind?
- Moles are not blind; they have eyes.
- However, they have very poor vision and rely primarily on their senses of smell and touch to navigate the underground environment.
- The eyes of a mole are small and covered by a layer of dark fur. They are useless for practical vision, but can detect light and dark.
- Moles use their sense of smell for navigation, foraging for food, and detecting predators.
- They also have sensitive whiskers that help them feel their way through the dark subterranean environment.
- As a result, moles are able to lead fairly active lives underground, despite their poor eyesight.
Are moles dangerous to humans?
- Moles do not pose any threat to humans.
- Moles are not venomous and do not bite.
- Moles are not known to carry any diseases.
- Moles generally do not cause any harm to humans.
Moles are solitary animals that prefer to remain out of sight and away from people. They are not known to attack humans and generally avoid contact with them. Moles are not venomous and do not bite, so they are not dangerous to humans. Furthermore, moles are not known to carry any diseases, and so they pose no threat to humans. As a result, moles generally do not cause any harm to humans.
Is there any way to tell if a mole is alive or dead?
- Check for movement. A live mole will exhibit active movement, while a dead one will not.
- Look for signs of breathing. Gently observe the area around the mole’s nose and mouth. If you see any shallow movements, it is likely still alive.
- Look for signs of life in the eyes. If the eyes are open and unresponsive, it is likely dead.
- Observe the color of the mole. If it is pale or grey, this is an indication of death.
- Check for a heartbeat. Place your hand on the mole’s chest and press lightly. If there is a faint heartbeat, the mole is alive.
How do moles behave in the wild?
Moles are solitary animals that spend most of their time burrowing underground for food. They dig tunnels and create mounds of dirt as they search for insects, earthworms, and other prey. Moles also use their tunnels to hide from predators. During the day, moles are usually inactive and remain in their burrow, coming out at night to forage for food. When threatened, moles will flee to their burrow or hide in the grass.
Conclusion
Moles do not have eyes, but they use other senses such as smell and hearing to navigate and find food. Despite their lack of vision, moles are highly adapted to life underground and can live in a variety of conditions. With their special adaptations and behaviors, moles can survive and thrive in their environment.