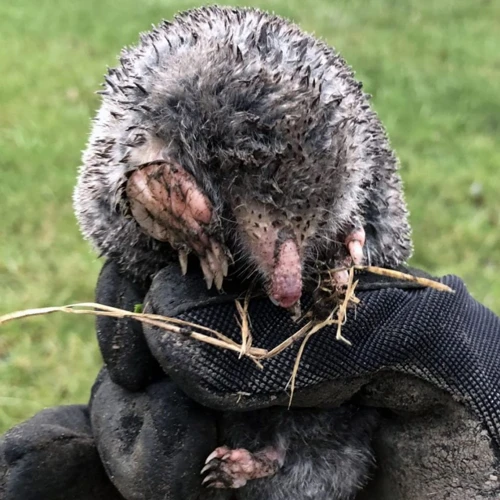
As gardeners, we may have encountered the difficulties of dealing with pests that damage our garden and lawn. One of the culprits that we may come across are the moles. Despite their small size, these creatures can cause significant damage to our outdoor spaces. But what exactly do moles eat? This is a question that perplexes many of us, as we try to find ways to control their eating habits. In this article, we will delve into the eating habits of moles and explore the impact of their diet on our gardens and lawns. We will also provide tips on how to control their eating habits and maintain a healthy outdoor space.
Diet of Moles
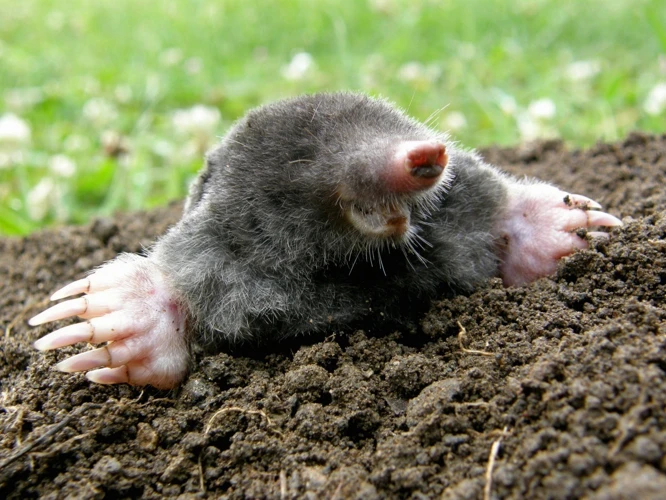

It’s always fascinating to learn about the dietary habits of different animals, and moles are no exception. These small, burrowing creatures have a unique diet that’s tailored to their subterranean lifestyle. Moles’ diets consist primarily of insects, worms, and small animals. However, their exact diet and hunting techniques can vary depending on the time of year and other factors. To truly understand a mole’s diet, we need to explore the animals’ underground world and learn about their habits and preferences. If you’re curious about what moles like to feast on, keep reading. And if you want to learn more about moles’ burrowing habits, check out our article on moles’ burrowing habits in depth.
Underground Creatures
Moles are known for their distinctive feeding habits and the primary source of their diet is the variety of small creatures that live beneath the ground. In this section, we will take a closer look at some of the underground creatures that moles prefer to hunt and consume using an HTML table:
| Underground Creatures | Details |
|---|---|
| Earthworms | One of the favorite foods of moles, earthworms make up a considerable portion of their diet. Moles tend to go for larger earthworms, which provides them with more nutrition. |
| Grubs | Grubs, also known as beetle larvae, are another high-protein food source for moles. They are usually easier to catch since they do not squirm around as much as earthworms do. |
| Insects | Moles also prey on a wide range of insects, including ants, beetles, and centipedes. Moles have sharp teeth and can easily crush the exoskeletons of these small creatures. |
| Small rodents | While moles primarily feed on invertebrates, they occasionally prey on small rodents like mice and voles. Moles have been known to catch and eat rodents when these creatures invade their underground burrows. |
Moles’ preference for a diet that is abundant in underground creatures is understandable, as they are burrowing mammals that live their entire lives beneath the surface of the ground. Their sharp senses and broad forepaws make them expert hunters and diggers.
Understanding the eating habits of moles is essential to managing and controlling their population. By taking proactive measures to limit their food supply, homeowners can reduce the damage caused by these shelter-seeking creatures. For more information on mole behavior and daily routines, check out our detailed article on /moles-daily-routines/.
Insects and Worms
Insects and worms are a crucial part of a mole’s diet. These small creatures are abundantly found in the soil and are easily accessible to the burrowing mammal. Moles have a strong sense of smell and can detect insects and worms from a distance. They use their sharp claws to dig through the soil and create tunnels to reach their prey.
Below is a table that highlights some of the insects and worms that moles typically feed on:
| Insects | Worms |
|---|---|
| Ants | Earthworms |
| Beetles | Nightcrawlers |
| Caterpillars | Red wigglers |
| Cricket | Grubs |
| Grasshoppers | Mealworms |
It is fascinating to see how moles have adapted to their habitat and developed a taste for insects and worms. These creatures are a great source of protein, which makes them an essential part of a mole’s diet. If you want to read more about moles and their habits, check out our article on moles’ social habits.
Small Animals
Moles are not strictly insectivorous, and will occasionally prey on small animals. Although this is a small portion of their diet, it is still significant. These small animals can include rodents, birds, and even small reptiles or amphibians. Moles may also eat other small burrowing mammals such as shrews or voles.
Studies have shown that moles are highly skilled at detecting their prey, using their keen sense of smell and specialized hearing to locate small animals even beneath the soil. Once they have detected their prey, moles use their powerful front claws to dig through the soil and capture them. It is important to note, however, that small animals do not make up the majority of a mole’s diet.
Below is a table summarizing the different types of food that moles consume, including small animals:
| Food Source | Percentage of Diet |
|---|---|
| Insects and Worms | 70-80% |
| Small Animals | 10-15% |
| Plant Material | 5-10% |
| Other Sources | 5-10% |
It is clear that while small animals do make up a portion of the mole’s diet, they are not the primary source of food. Moles are predominantly insectivorous and feed on insects and worms. To learn more about the different habits of moles, such as their sleeping, mating, and hunting habits, click the relevant links.
Seasonal Changes in Their Diet

As with many other animals, moles’ eating habits change according to seasonal availability of food. In the spring, moles’ diet consists primarily of insects and worms, which are easier to find due to increased soil moisture from rain. Moles are known to consume a wide variety of insects, including beetles, ants, and grasshoppers. However, earthworms are their favorite food and they can eat up to their body weight in worms each day.
In the summer, moles’ diet shifts more towards small animals. Moles have been observed feeding on small rodents, such as shrews and voles. They also eat birds, frogs, and reptiles, although these make up a smaller proportion of their diet.
In the fall, as temperatures begin to cool and soil moisture decreases, moles’ diet returns to a greater proportion of insects and worms. They will also consume more plant material during this season, including roots, bulbs, and tubers.
Winter is a challenging season for moles, as the ground may be frozen and covered with snow, reducing the availability of insects and small animals. During this time, moles may eat stored food or rely on fat stores they have built up during the summer and fall. Moles are known to have a slow metabolism during the winter months, as they conserve energy and try to avoid starvation.
Understanding moles’ seasonal changes in diet is important for those trying to control mole populations. For example, trapping and repelling may be more effective during seasons when moles are consuming larger amounts of insects and worms. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lawn that is free of grubs and other insects may reduce the attractiveness of the area for moles.
Moles have a diverse diet that shifts according to seasonal availability of food. To learn more about moles, you can read about their sleeping habits here.
Impact of Moles’ Eating Habits

The eating habits of moles have a significant impact on their surrounding environment. These subterranean creatures play a crucial role in the ecosystem by consuming a variety of food sources. However, their search for food can cause damage to lawns and gardens. The impact of moles’ eating habits goes beyond surface-level damage and can affect the health of soil and plant growth. In this article, we will explore the consequences of moles’ eating habits and potential solutions to mitigate any negative effects. For more information on moles, see our articles on mole mating habits and moles’ hunting habits.
Gardening and Lawn Damage
When it comes to the eating habits of moles, it’s important to understand the potential damage they can cause to your garden and lawn. Moles have a strong appetite for insects and worms, which can decimate the soil quality and root systems of your plants. This means that if you have a mole infestation in your yard, your gardening efforts may be in jeopardy.
One of the most obvious signs of mole presence is the effect on your lawn. Moles burrow and tunnel beneath the surface, causing significant damage to the roots of your grass. As they do so, they create mounds of excavated soil that can be an eyesore on an otherwise pristine lawn. If left alone, moles can continue to cause damage and kill off large areas of your lawn.
In addition to the physical damage caused by their burrowing, moles can also attract other pests to your yard. As they feed on insects and worms, they may also be inviting other animals that prey on these creatures, like skunks and raccoons. This can lead to a cascading effect of damage and make it even more difficult to maintain a healthy garden and lawn.
If you notice signs of a mole infestation, it’s important to take action quickly. There are a variety of methods for trapping and repelling moles, but it’s important to take care not to harm other wildlife in the process. Maintaining a healthy lawn and soil can help prevent moles from taking up residence in the first place.
The impact of moles’ eating habits on your gardening and lawn efforts can be significant. By being aware of the signs of a mole infestation and taking action to control their presence, you can help protect your plants and maintain a beautiful outdoor space.
Soil and Plant Health
The eating habits of moles not only impact gardens and lawns but also have a significant effect on soil and plant health. Moles dig intricate tunnels beneath the ground in search of food, and their digging behavior can loosen the soil and increase aeration. This can be beneficial for plant growth, as it allows better penetration of water and nutrients to the roots. Additionally, moles’ burrowing can help break up compacted soil, which can improve drainage and reduce erosion.
However, at the same time, moles can also harm soil and plant health. Their tunnels can create air pockets that cause roots to dry out, leading to plant stress and ultimately death. Moles often feed on insects, and some of these insects are actually beneficial to plants. For example, earthworms help break down organic matter in soil and provide nutrients to plants. So when moles consume these earthworms, it can disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem, leading to nutrient-poor soil and poor plant growth.
To summarize the impacts of moles’ eating habits on soil and plants, we can use a table like this:
| Positive Impacts | Negative Impacts |
| Increased soil aeration | Dried-out roots |
| Improved soil drainage | Disruption of ecosystem balance |
| Loosened soil | Nutrient-poor soil |
Moles’ eating habits can have both positive and negative impacts on soil and plant health. It’s important for gardeners and homeowners to be aware of these impacts and take appropriate measures to mitigate any negative effects while still maintaining a healthy and natural environment.
Controlling Moles’ Eating Habits
When it comes to controlling the eating habits of moles, many homeowners find themselves perplexed. While moles play an essential role in maintaining soil health, they can also wreak havoc on lawns and gardens. There are various methods for controlling these subterranean creatures, but each comes with its advantages and disadvantages. In this section, we will explore some of the most common ways to curb moles’ eating habits, including trapping and repelling, as well as maintaining a healthy lawn.
Trapping and Repelling
One of the ways to control moles’ eating habits is by trapping them. There are different types of traps available in the market. Some traps are lethal while others are humane. Lethal traps kill the moles, while humane traps trap them alive, allowing for their release in a different location.
Another way to control moles is repelling them. There are different repellents available, including natural and synthetic options. Natural repellents such as castor oil and garlic are effective in deterring moles. These repellents work by making the soil or environment unattractive to moles.
Synthetic repellents such as those containing aluminum ammonium sulfate and naphthalene are also effective. These types of repellents work by stimulating the sensory receptors of moles, deterring them from the area.
However, it is important to note that repellents are only effective for a limited time, and their effectiveness may decrease over time. The use of repellents may have adverse effects on other animals and plants in the environment.
| Trapping | Repelling |
|---|---|
| Lethal traps | Natural repellents |
| Humane traps | Synthetic repellents |
| Effective in eliminating moles | Makes soil or environment unattractive to moles |
| May require professional help to set up | May have adverse effects on other animals and plants |
Note that trapping is generally considered to be more effective than repelling in controlling moles, as trapping eliminates the problem rather than just temporarily deterring it. However, trapping may require professional help to set up, and it also comes with ethical concerns regarding the humane treatment of animals.
Maintaining a Healthy Lawn
A key factor in controlling moles’ eating habits is maintaining a healthy lawn. Moles are attracted to yards with lush grass and plenty of insects to feast on. Here are some tips for keeping your lawn healthy and less appealing to moles:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Mow regularly | Moles prefer taller grass, so keeping your lawn trimmed can help deter them. |
| Aerate your lawn | Compacted soil can make it difficult for grass roots to grow and can attract insects, which in turn attracts moles. Aerating your lawn can help oxygen, water, and nutrients get to the roots and prevent compacted soil. |
| Remove thatch | Thatch is a buildup of dead grass and other organic material that can create a habitat for insects and moles. Rake up excess thatch to prevent this. |
| Limit watering | Overwatering your lawn can create a damp environment that is attractive to insects and moles. Only water when necessary and avoid saturating the soil. |
By following these tips, you can help make your lawn less attractive to moles and discourage them from feasting on the insects and worms in your yard. This can ultimately help control their eating habits and prevent damage to your lawn and garden.
Conclusion
After exploring the eating habits of moles, it becomes evident that these small creatures have a significant impact on the environment they live in. Although they primarily feast on underground creatures, insects, and worms, they also consume small animals during certain seasons.
Their diet can cause damage to gardens and lawns, affecting the health of soil and plants. Moles’ eating habits can severely impact the ecosystem by disrupting the soil’s structure, which can lead to soil erosion.
Controlling moles’ eating habits requires a combination of trapping and repelling techniques, as well as maintaining a healthy lawn. It’s important to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage to the environment.
In conclusion, understanding the eating habits of moles is crucial when dealing with these small but impactful creatures. Controlling their eating habits can have a significant impact on the environment, and it’s essential to take action to preserve your lawn, garden, and the health of the surrounding ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do moles like to eat?
Moels mainly feed on underground creatures like earthworms and insects, as well as small animals like mice and shrews.
Do moles eat plants?
No, moles do not eat plants. They are carnivorous and prefer to feed on insects, earthworms, and other small animals.
How do moles find their food?
Moles have very sensitive noses and can detect the scent of their prey underground. They use their front paws to dig tunnels and locate their food.
Do moles hibernate in winter?
No, moles do not hibernate in winter. They are active year-round, although they may dig deeper tunnels in winter to avoid freezing temperatures.
Can moles cause damage to lawns and gardens?
Yes, moles can damage lawns and gardens by digging tunnels and uprooting plants. Their burrowing can also create uneven terrain and tripping hazards.
How can I tell if I have a mole problem in my lawn?
You may notice raised ridges or molehills in your lawn, as well as areas of dead or dying grass. Moles may also leave large holes or tunnels visible on the surface.
What are some natural ways to repel moles?
Some natural methods of repelling moles include using castor oil, peppermint oil, or garlic, as well as planting daffodils or marigolds in your garden.
What is the best way to trap moles?
Trapping moles can be done with various kinds of traps, including scissor traps and harpoon traps. It’s important to set the traps in the right location and at the right depth to be effective.
What are the long-term effects of moles on soil and plant health?
Moles can have both positive and negative effects on soil and plant health. Their burrowing can help to aerate soil and improve drainage, but it can also disrupt root systems and create areas of dry, compacted soil.
Are there any risks to using chemicals to control moles?
Chemical control methods for moles can pose risks to other wildlife, pets, and humans. It’s important to follow instructions carefully and use them only as a last resort.