Are you wondering about the differences between a groundhog and a mole? Do you want to know which one is which? If so, then you’ve come to the right place. This article will explore the differences between these two burrowing animals, so you can easily identify a groundhog vs mole when you see one.
Overview of Groundhogs
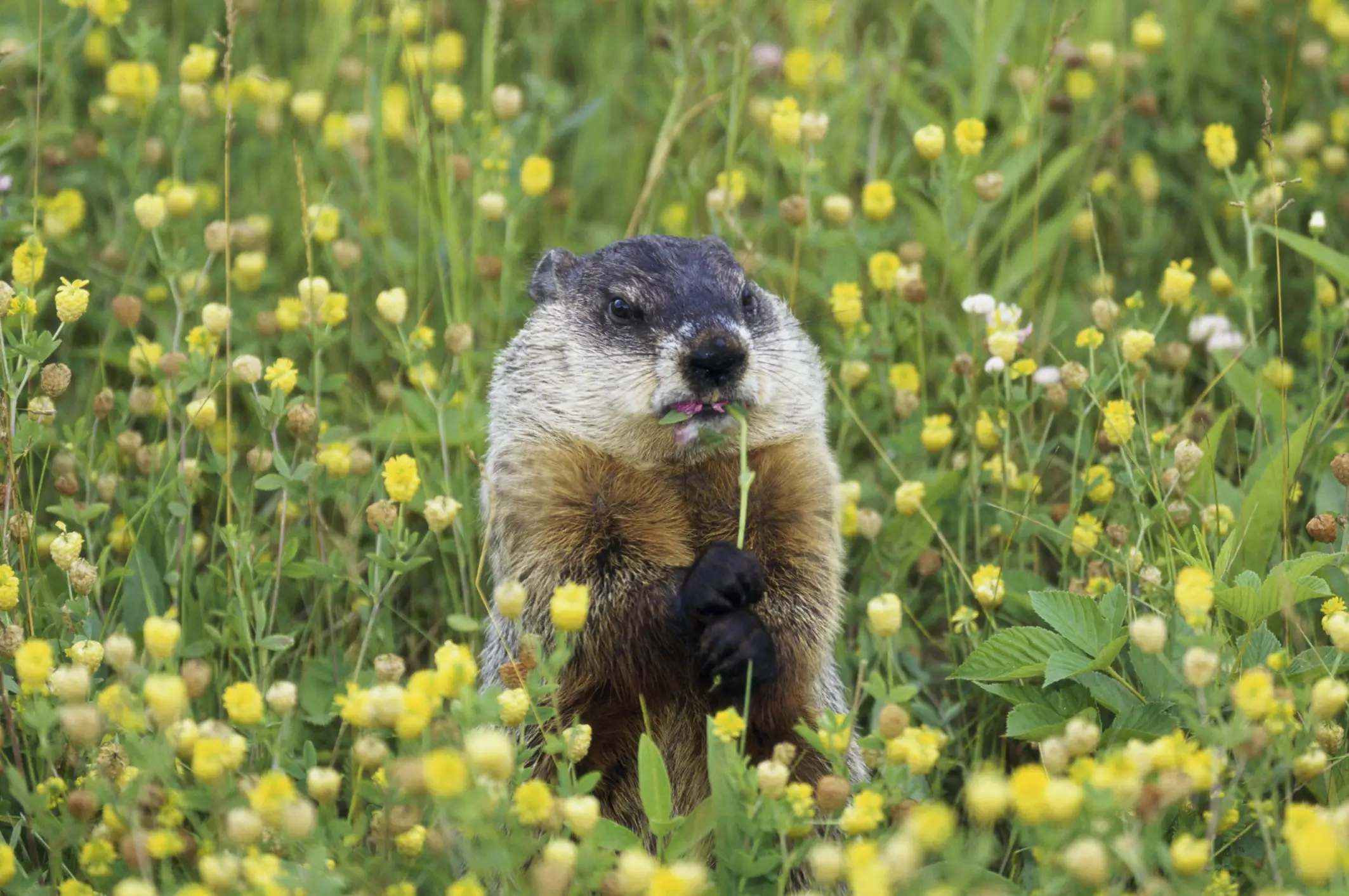

Appearance
Groundhogs, also known as woodchucks, are burrowing rodents that are native to North America. They have a stout body, short legs, and a small head with a white stripe running from their eyes to the back of their neck. They have short, dense fur that is usually a shade of brown, and they can reach up to 26 inches in length, with a tail adding another four to seven inches.
Habits
Groundhogs are typically active during the day and spend most of their time foraging for food. They are excellent diggers and are known to create burrows that can be up to five feet deep and 30 feet long. These burrows provide them with shelter from predators and a place to hibernate during the winter.
Diet
Groundhogs are herbivores and primarily feed on grasses and other vegetation. During the summer, they will also eat fruits, nuts, and insects. They have been known to consume small animals, such as mice and birds, but this is rare. Their diet is largely similar to that of moles, making moles vs groundhog a common comparison.
Overview of Moles
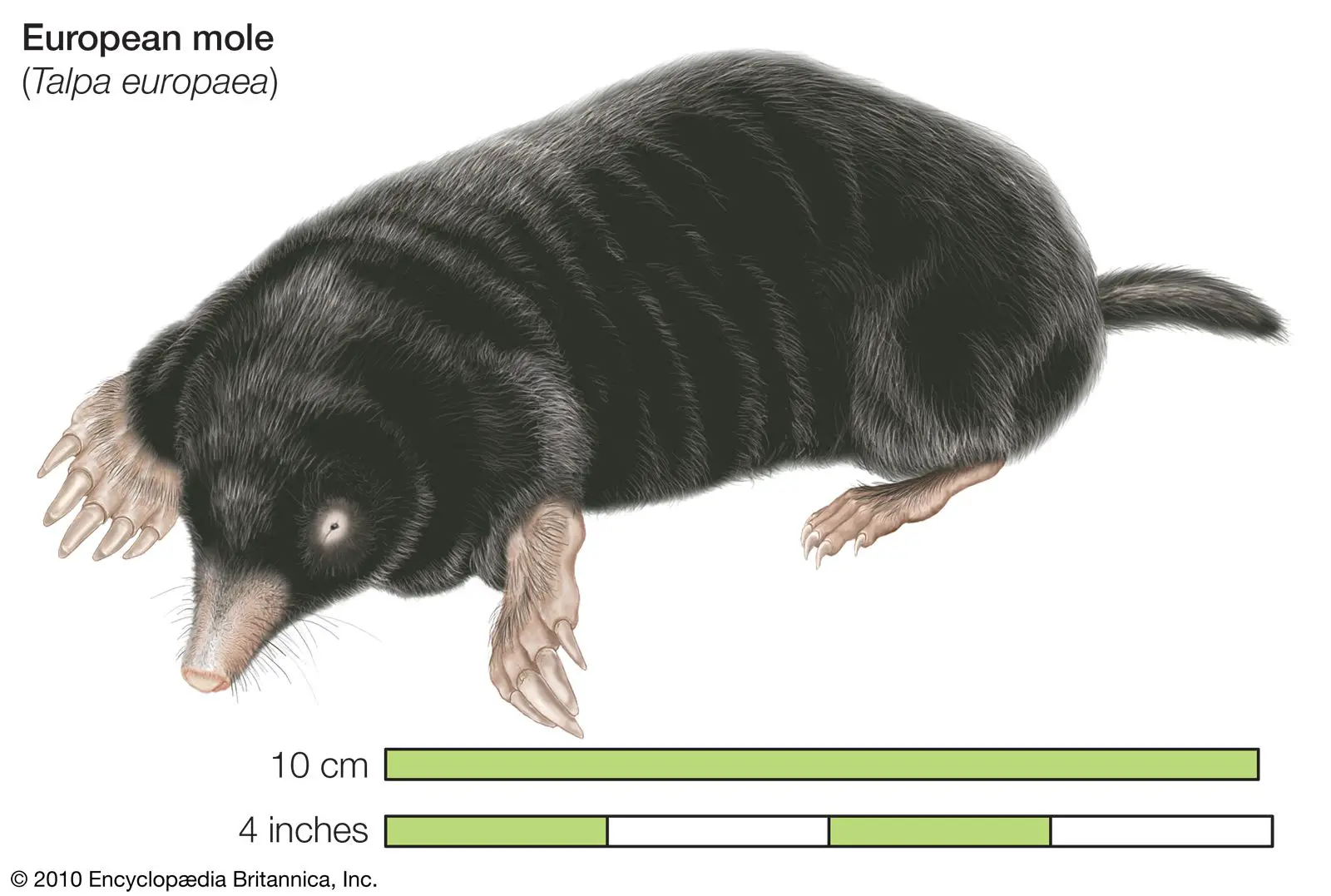
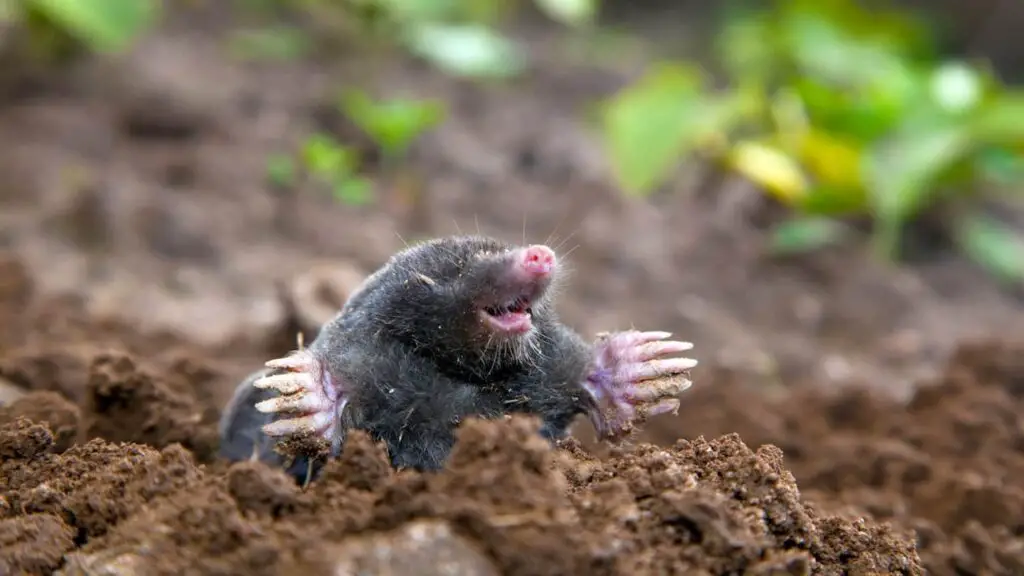
Appearance
Moles are small, dark-colored animals with velvety fur, shovel-like front feet, and small eyes. They have small, pointed snouts and a thick, cylindrical body. Their size ranges from 6 to 8 inches in length. Moles are often confused with gophers and groundhogs, but they have distinct differences in their physical appearance.
Habits
Moles primarily live in underground burrows and tunnels, where they can find a safe and protected environment. They are solitary animals and are rarely seen above ground. During the day, moles spend most of their time under the soil, where they actively search for food and create their burrows.
Diet
Moles primarily feed on earthworms, insects, and other small invertebrates. They have specially adapted teeth and claws which help them to capture and consume their prey. Occasionally, moles may also feed on plant roots and tubers.
Habitat Differences
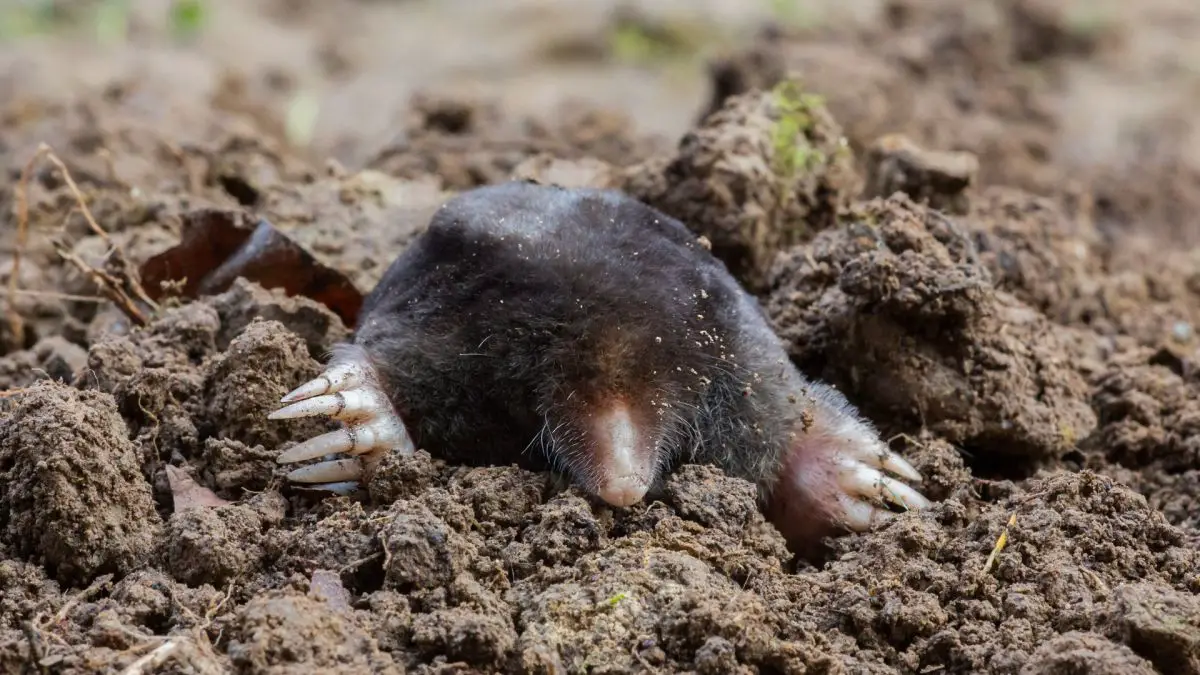

Groundhogs and moles are both small, burrowing mammals, but they have very different habitats. Groundhogs are found in open, grassy areas such as fields, pastures, and meadows. They also inhabit areas around roads, farms, and gardens. Moles, on the other hand, prefer a more secluded environment and are typically found in shady, moist areas like forests and woodlands.
- Groundhogs are found in open, grassy areas such as fields, pastures, and meadows.
- Moles prefer shady, moist environments like forests and woodlands.
- Groundhogs inhabit areas around roads, farms, and gardens.
Groundhogs can dig burrows up to five feet deep and twenty-five feet long, while moles typically stay close to the surface and construct tunnels that are usually no more than three inches below ground. The tunnels of groundhogs are often visible and can cause damage to gardens and lawns. Moles, however, are mostly hidden and rarely cause any damage.
The habitats of groundhogs and moles have a direct impact on the kinds of food they eat. Groundhogs feed on grasses, weeds, and other vegetation found in their open, grassy habitats. Moles, on the other hand, feed mainly on earthworms, grubs, and other small insects found in their moist, forested environments.
Overall, groundhogs and moles inhabit very different habitats and have unique dietary needs. Though they may look similar, groundhogs and moles are very different animals and should not be confused.
Mating Habits
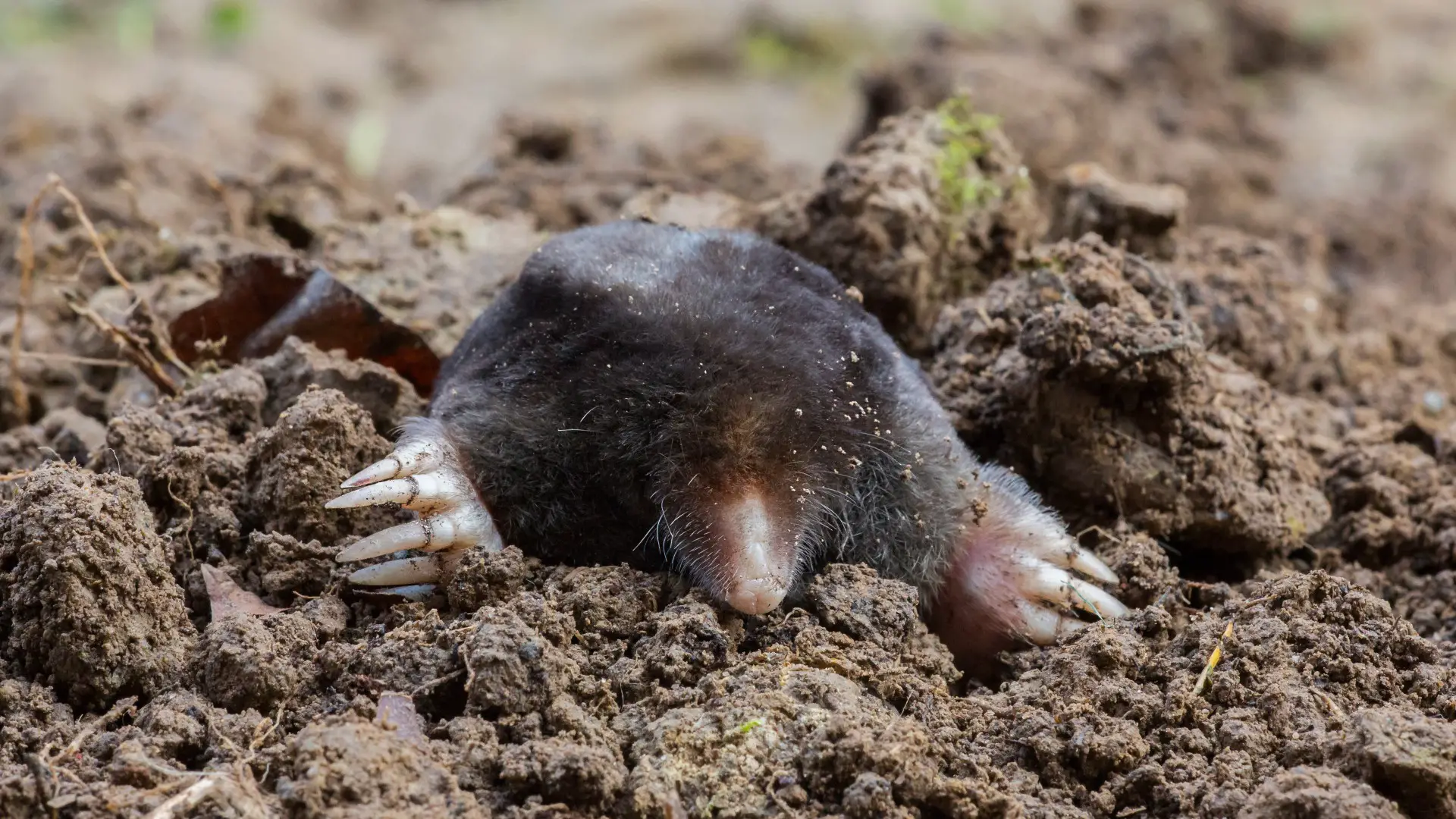

- Groundhogs mate in March and April, and the female will give birth to her young in April or May. The litter size is usually 3-8 kits.
- Moles breed in the spring and summer months and the female will give birth to her young in May or June. The litter size is usually 1-7 kits.
The mating habits of groundhogs and moles differ significantly. Groundhogs are polygynous and mate with more than one female, while the moles are monogamous and mate with only one female. Groundhogs are typically more aggressive and territorial during mating season and will fight off intruders to protect their territory. Moles, on the other hand, are passive during the mating season and will not defend their territory.
Predation
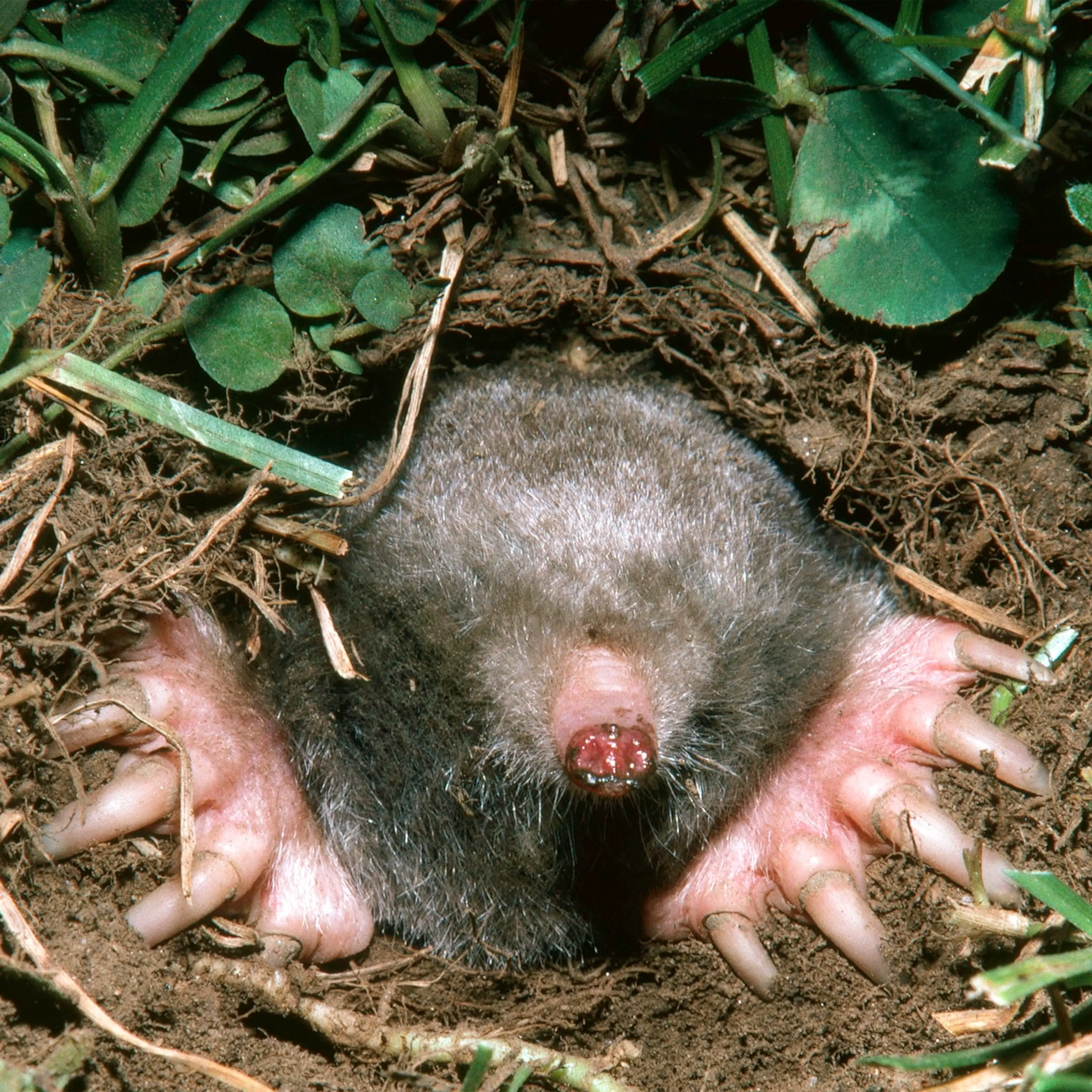

- Groundhogs are more likely to be the predators in their environment than moles. They are omnivores, meaning they feed on both plants and animals.
- Moles are insectivores, meaning they feed mainly on insects and worms. They are unlikely to attack a groundhog, but may eat the eggs or young of groundhogs if they can find them.
- Groundhogs can cause damage to plants and small animals while they search for food, while moles can cause damage to lawns and gardens while they tunnel through the soil.
- Groundhogs are more likely to be killed by their predators than moles. Predators of groundhogs include hawks, owls, foxes, coyotes, dogs, and cats.
- Moles are relatively safe from predators, as their tunnels provide them with a safe haven from most predators. However, moles can still be killed by cats, dogs, and other small predators who can fit into their tunnels.
Groundhog vs Mole: Comparative Chart
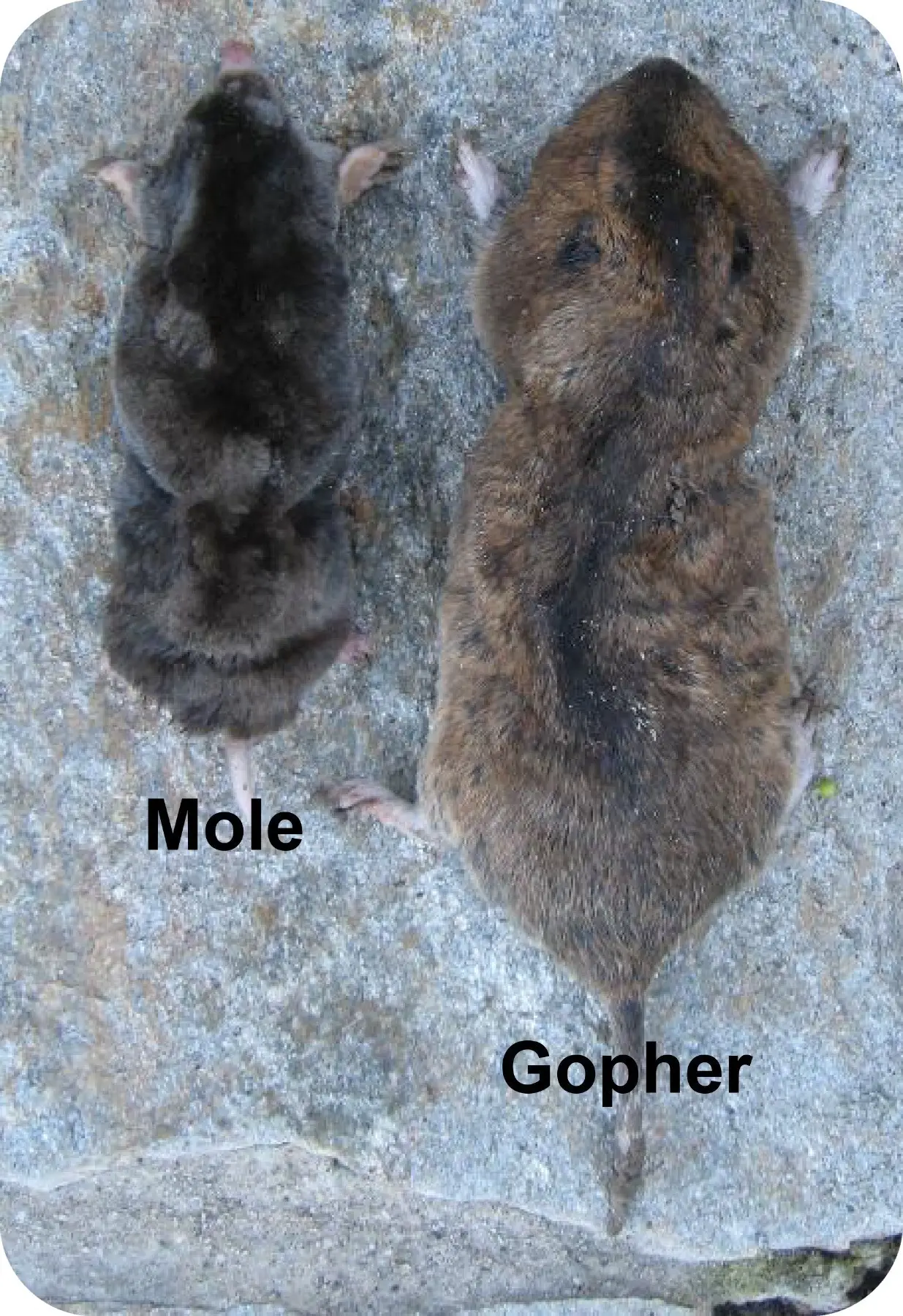

- Physical Appearance: Groundhogs are reddish-brown in color and have a white line down the back of their bodies. They have short, stocky legs and a long, furry tail. Moles have black fur and have long, pointed snouts and shovel-like front feet.
- Habitat: Groundhogs live in open fields and meadows and are found in North America. Moles are found in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, and live in underground burrows.
- Diet: Groundhogs are herbivores and feed mainly on grasses and other plants. Moles are insectivores and feed mainly on earthworms, grubs, and other insects.
- Behavior: Groundhogs are active during the day and tend to be solitary animals, although they may form small colonies. Moles are active both day and night and are solitary, but may live in groups of up to eight individuals.
- Reproduction: Groundhogs breed in the spring and have litters of up to six young. Moles breed in the early summer and have litters of up to six young.
FAQs
QA
| What is the difference between a groundhog and a mole? | A groundhog, also known as a woodchuck, is a large rodent belonging to the marmot family. They have short, powerful legs, short ears, and a short, furry tail. Moles are small mammals that belong to the Talpidae family. They have small, narrow heads, short, powerful legs and short, velvety fur. They are adapted to living underground. |
| What do groundhogs and moles eat? | Groundhogs are herbivores and eat grass, leaves, fruits and nuts. Moles are insectivores, and primarily feed on earthworms, grubs, and other insects. |
| Are groundhogs and moles dangerous? | Groundhogs are generally not considered dangerous to humans, but they can be aggressive if they feel threatened. Moles are not considered dangerous and can be handled safely. |
| Where do groundhogs and moles live? | Groundhogs are generally found in open meadows, pastures, and woodlands. Moles live in underground tunnels, and can be found in gardens and lawns. |
Frequently Asked Questions
How do groundhogs and moles differ in size?
- Groundhogs
-
- are much larger than moles. They can reach up to 20 inches (50 cm) in length and weigh up to 10 pounds (4.5 kg).
- Moles are much smaller, usually reaching only 5 inches (13 cm) in length and weighing about 4 ounces (113 g).
Groundhogs have short, coarse fur that is brown or gray in color. Moles, on the other hand, have silky, black fur.
What type of habitats do groundhogs and moles prefer?
Groundhogs prefer habitats with enough open ground to build their burrows. They are found in fields, meadows, and pastures with some trees or shrubs nearby for cover.
Moles, on the other hand, prefer habitats with moist soils and plenty of vegetation, such as wetlands, grasslands, and woodlands. They can also be found in gardens, lawns, and fields.
- Groundhogs prefer habitats with enough open ground to build their burrows, such as fields, meadows, and pastures with some trees or shrubs nearby.
- Moles prefer habitats with moist soils and plenty of vegetation, such as wetlands, grasslands, and woodlands.
- They can also be found in gardens, lawns, and fields.
What are the main physical differences between groundhogs and moles?
Groundhogs are larger than moles, typically between 18-24 inches long. They have short legs and long bodies, with long, coarse fur. They have four long claws on their front paws, and two on their hind paws. Moles, on the other hand, are much smaller, usually between 5-8 inches long. They have a cylindrical body and velvety fur, with five toes on each foot and large, paddle-shaped front feet. They also have small eyes, ears, and nostrils, as well as long, powerful claws used for digging.
How do groundhogs and moles behave differently?
Groundhogs are active during the day and their main activity is foraging for food, while moles are active mostly at night and mainly stay underground. Groundhogs are social animals, living in colonies, while moles are solitary. Groundhogs are also quite vocal, making noises to communicate with each other, while moles make very little sound. Furthermore, groundhogs are excellent climbers and swimmers, while moles are not.
What Food Do Groundhogs and Moles Eat?
Groundhogs are herbivores that mainly feed on grasses, clover, and other plants. They will also eat fruits and vegetables, as well as insects and other small animals. Moles are also mainly insectivores, feeding on worms, grubs, and other small insects. They will also feed on small mammals, such as mice, voles, and shrews.
Conclusion
Moles and groundhogs are two distinct animals that can be mistaken for one another. While they share certain similarities, these animals have distinct physical and behavioral differences which makes them easy to identify. Groundhogs are much larger than moles, and they are primarily terrestrial animals that dig burrows in the ground. On the other hand, moles are small, solitary creatures that live underground and feed on insects and worms. Both of these animals can be a nuisance in yards and gardens, but understanding the differences between them can help to identify the best way to manage them.
References
- Difference between Groundhog and Mole – Audubon
- Difference between Groundhog and Mole – The Spruce
- Groundhog – Wikipedia